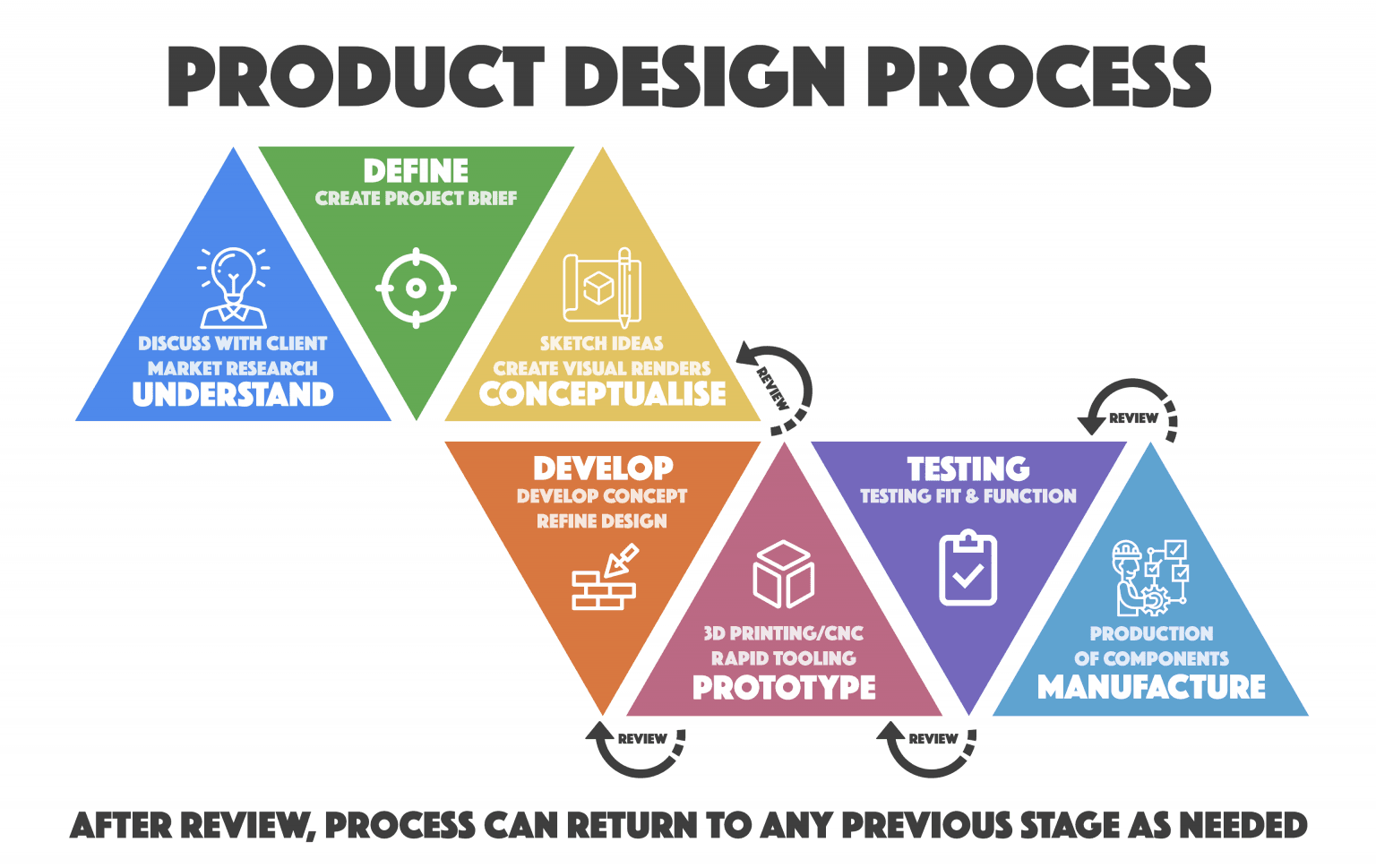
Our Three Step Process
October 7, 2024
Reverse Engineering: A Tool for Innovation or Reinvention?

Our Three Step Process
October 7, 2024
Reverse Engineering: A Tool for Innovation or Reinvention?
Discover how reverse engineering serves as a catalyst for innovation and reinvention in product development. This article explores strategies, challenges, and ethical considerations, highlighting NorthnStar's expertise in leveraging reverse engineering responsibly.
Is reverse engineering merely a means to replicate existing products, or can it be a powerful catalyst for innovation and reinvention? By deconstructing products and systems, we can uncover insights that drive technological advancement and competitive advantage. Let's explore how reverse engineering serves as a tool for both innovation and reinvention.
At NorthnStar, we've encountered numerous clients intrigued by the potential of reverse engineering. They often face challenges in understanding complex technologies, improving upon existing products, or entering markets dominated by established players. Recognizing the strategic value and ethical considerations of reverse engineering, we've developed approaches to help them leverage this tool effectively. This article delves into the role of reverse engineering in product development, sharing insights from our experiences to guide you in harnessing its power for innovation and reinvention.
Understanding Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering involves dissecting a product or system to understand its components, architecture, and functioning. It's a process of deconstruction that reveals the intricacies of design and technology, enabling businesses to learn from existing solutions.
Applications of Reverse Engineering:
Product Improvement: Identifying weaknesses or limitations in a product to enhance performance.
Technology Learning: Gaining insights into advanced technologies used by competitors.
Legacy System Support: Maintaining or updating systems with obsolete documentation.
Innovation Catalyst: Inspiring new ideas by understanding how existing products work.
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights: Respecting patents, copyrights, and trade secrets is crucial.
Fair Use: Reverse engineering for interoperability or research may be permissible under certain conditions.
Compliance: Ensuring that the process adheres to relevant laws and industry regulations.
Case Study: Innovating Through Reverse Engineering in the Automotive Industry
Client Challenge:
An automotive parts manufacturer approached us with the goal of entering the electric vehicle (EV) market. They lacked expertise in EV technology and faced significant barriers due to proprietary technologies held by established competitors. They sought to understand the design and functionality of leading EV components to develop compatible and competitive products. Acknowledging the legal and ethical complexities, they turned to our expertise to navigate reverse engineering responsibly.
Our Approach:
We aimed to help the client leverage reverse engineering as a tool for innovation while ensuring compliance with all legal and ethical standards. Our multidisciplinary team collaborated with legal advisors, engineers, and industry experts to structure a strategic plan.
Actions Taken:
Feasibility Assessment:
Legal Review: Evaluated patents and IP protections related to target components.
Ethical Considerations: Established guidelines to prevent infringement and unethical practices.
Market Analysis: Identified opportunities where innovation could meet unmet needs.
Target Selection:
Component Identification: Chose specific parts with expired patents or without IP restrictions.
Focus on Improvement Areas: Targeted components known for performance issues or high failure rates.
Reverse Engineering Process:
Disassembly and Documentation:
Carefully disassembled components to study materials, construction, and design.
Documented findings meticulously, creating detailed diagrams and notes.
Analysis and Testing:
Performed material analysis to understand properties and limitations.
Conducted performance testing to benchmark against industry standards.
Innovation and Redesign:
Idea Generation:
Brainstormed enhancements based on insights gained.
Considered alternative materials, designs, and technologies to improve performance.
Prototyping and Development:
Developed prototypes incorporating innovative features.
Tested prototypes rigorously to ensure reliability and compatibility.
Compliance and Validation:
Legal Verification:
Ensured that new designs did not infringe on existing IP.
Filed for patents on novel innovations developed.
Certification:
Obtained necessary industry certifications and approvals.
Market Entry Strategy:
Value Proposition Articulation:
Highlighted improved performance, cost-effectiveness, or unique features.
Positioned products to meet specific market needs unmet by competitors.
Partnership Development:
Established relationships with EV manufacturers and suppliers.
Created collaborative opportunities for further innovation.
Outcome:
Successful Product Launch:
Introduced a line of EV components that offered superior performance and reliability.
Gained market traction by filling gaps left by competitors.
Innovation Recognition:
Received industry accolades for innovative designs.
Secured patents for new technologies developed.
Business Growth:
Expanded client portfolio and increased revenue streams.
Established the client as a credible player in the EV market.
Key Takeaways:
Strategic Targeting: Focusing on components with opportunities for innovation minimizes legal risks and maximizes impact.
Ethical Practices: Adhering to legal and ethical standards builds trust and long-term success.
Value Addition: Using reverse engineering to innovate rather than merely replicate creates competitive advantages.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involving legal, technical, and market experts ensures a holistic approach.
Reverse Engineering as a Tool for Innovation
1. Enhancing Existing Products
Identifying Limitations: Understanding weaknesses in current products opens avenues for improvement.
Incorporating New Technologies: Integrating advanced materials or technologies can elevate product performance.
2. Accelerating R&D
Learning from Competitors: Gaining insights into industry standards and best practices speeds up development.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Understanding why certain designs fail helps in avoiding similar mistakes.
3. Fostering Innovation
Inspiration Source: Existing products can spark ideas for entirely new solutions.
Cross-Industry Applications: Applying concepts from one industry to another can lead to breakthrough innovations.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
1. Intellectual Property Risks
Challenge: Unintentionally infringing on patents or copyrights.
Solution: Conduct thorough IP research and consult legal experts.
2. Trade Secret Violations
Challenge: Accessing proprietary information unlawfully.
Solution: Ensure all information is obtained legally and ethically.
3. Ethical Dilemmas
Challenge: Balancing competitive advantage with fair business practices.
Solution: Establish clear ethical guidelines and adhere to industry codes of conduct.
4. Technical Complexities
Challenge: Reverse engineering sophisticated or proprietary technologies.
Solution: Invest in skilled personnel and advanced tools for accurate analysis.
5. Resource Intensity
Challenge: Reverse engineering can be time-consuming and costly.
Solution: Evaluate the return on investment and focus on high-impact areas.
Strategies for Responsible Reverse Engineering
1. Legal Due Diligence
Patent Searches: Identify existing patents and understand their scope.
Consult Legal Experts: Ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
2. Ethical Framework Establishment
Code of Conduct: Define ethical boundaries and expectations.
Transparency: Maintain open communication about methods and intentions.
3. Focus on Innovation
Value Addition: Aim to improve upon existing designs, not just replicate them.
Original Contributions: Develop unique features or technologies.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Interdisciplinary Teams: Involve experts from engineering, legal, and business fields.
Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of learning and innovation.
NorthnStar's Expertise in Reverse Engineering
At NorthnStar, we offer comprehensive services to help clients leverage reverse engineering responsibly and effectively.
Our Services Include:
Legal and Ethical Guidance: Ensuring compliance with IP laws and ethical standards.
Technical Analysis: Utilizing advanced tools and expertise to dissect and understand products.
Innovation Development: Transforming insights into innovative designs and solutions.
Prototyping and Testing: Building and validating new products based on reverse engineering findings.
Market Strategy Support: Assisting in positioning and launching new products.
Client Success Story:
Our collaboration with the automotive parts manufacturer exemplifies how reverse engineering can serve as a tool for innovation rather than mere replication. By focusing on adding value and adhering to ethical practices, we helped the client achieve significant market success and contribute positively to the industry.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering, when used responsibly, is a powerful tool for innovation and reinvention. It enables businesses to learn from existing products, improve upon them, and develop new solutions that meet market needs.
At NorthnStar, we're committed to helping you harness the potential of reverse engineering ethically and effectively. Let us guide you in transforming insights into innovative products that drive success.
Interested in exploring how reverse engineering can fuel your innovation? Contact NorthnStar today, and let's embark on this journey together.
Is reverse engineering merely a means to replicate existing products, or can it be a powerful catalyst for innovation and reinvention? By deconstructing products and systems, we can uncover insights that drive technological advancement and competitive advantage. Let's explore how reverse engineering serves as a tool for both innovation and reinvention.
At NorthnStar, we've encountered numerous clients intrigued by the potential of reverse engineering. They often face challenges in understanding complex technologies, improving upon existing products, or entering markets dominated by established players. Recognizing the strategic value and ethical considerations of reverse engineering, we've developed approaches to help them leverage this tool effectively. This article delves into the role of reverse engineering in product development, sharing insights from our experiences to guide you in harnessing its power for innovation and reinvention.
Understanding Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering involves dissecting a product or system to understand its components, architecture, and functioning. It's a process of deconstruction that reveals the intricacies of design and technology, enabling businesses to learn from existing solutions.
Applications of Reverse Engineering:
Product Improvement: Identifying weaknesses or limitations in a product to enhance performance.
Technology Learning: Gaining insights into advanced technologies used by competitors.
Legacy System Support: Maintaining or updating systems with obsolete documentation.
Innovation Catalyst: Inspiring new ideas by understanding how existing products work.
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights: Respecting patents, copyrights, and trade secrets is crucial.
Fair Use: Reverse engineering for interoperability or research may be permissible under certain conditions.
Compliance: Ensuring that the process adheres to relevant laws and industry regulations.
Case Study: Innovating Through Reverse Engineering in the Automotive Industry
Client Challenge:
An automotive parts manufacturer approached us with the goal of entering the electric vehicle (EV) market. They lacked expertise in EV technology and faced significant barriers due to proprietary technologies held by established competitors. They sought to understand the design and functionality of leading EV components to develop compatible and competitive products. Acknowledging the legal and ethical complexities, they turned to our expertise to navigate reverse engineering responsibly.
Our Approach:
We aimed to help the client leverage reverse engineering as a tool for innovation while ensuring compliance with all legal and ethical standards. Our multidisciplinary team collaborated with legal advisors, engineers, and industry experts to structure a strategic plan.
Actions Taken:
Feasibility Assessment:
Legal Review: Evaluated patents and IP protections related to target components.
Ethical Considerations: Established guidelines to prevent infringement and unethical practices.
Market Analysis: Identified opportunities where innovation could meet unmet needs.
Target Selection:
Component Identification: Chose specific parts with expired patents or without IP restrictions.
Focus on Improvement Areas: Targeted components known for performance issues or high failure rates.
Reverse Engineering Process:
Disassembly and Documentation:
Carefully disassembled components to study materials, construction, and design.
Documented findings meticulously, creating detailed diagrams and notes.
Analysis and Testing:
Performed material analysis to understand properties and limitations.
Conducted performance testing to benchmark against industry standards.
Innovation and Redesign:
Idea Generation:
Brainstormed enhancements based on insights gained.
Considered alternative materials, designs, and technologies to improve performance.
Prototyping and Development:
Developed prototypes incorporating innovative features.
Tested prototypes rigorously to ensure reliability and compatibility.
Compliance and Validation:
Legal Verification:
Ensured that new designs did not infringe on existing IP.
Filed for patents on novel innovations developed.
Certification:
Obtained necessary industry certifications and approvals.
Market Entry Strategy:
Value Proposition Articulation:
Highlighted improved performance, cost-effectiveness, or unique features.
Positioned products to meet specific market needs unmet by competitors.
Partnership Development:
Established relationships with EV manufacturers and suppliers.
Created collaborative opportunities for further innovation.
Outcome:
Successful Product Launch:
Introduced a line of EV components that offered superior performance and reliability.
Gained market traction by filling gaps left by competitors.
Innovation Recognition:
Received industry accolades for innovative designs.
Secured patents for new technologies developed.
Business Growth:
Expanded client portfolio and increased revenue streams.
Established the client as a credible player in the EV market.
Key Takeaways:
Strategic Targeting: Focusing on components with opportunities for innovation minimizes legal risks and maximizes impact.
Ethical Practices: Adhering to legal and ethical standards builds trust and long-term success.
Value Addition: Using reverse engineering to innovate rather than merely replicate creates competitive advantages.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involving legal, technical, and market experts ensures a holistic approach.
Reverse Engineering as a Tool for Innovation
1. Enhancing Existing Products
Identifying Limitations: Understanding weaknesses in current products opens avenues for improvement.
Incorporating New Technologies: Integrating advanced materials or technologies can elevate product performance.
2. Accelerating R&D
Learning from Competitors: Gaining insights into industry standards and best practices speeds up development.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Understanding why certain designs fail helps in avoiding similar mistakes.
3. Fostering Innovation
Inspiration Source: Existing products can spark ideas for entirely new solutions.
Cross-Industry Applications: Applying concepts from one industry to another can lead to breakthrough innovations.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
1. Intellectual Property Risks
Challenge: Unintentionally infringing on patents or copyrights.
Solution: Conduct thorough IP research and consult legal experts.
2. Trade Secret Violations
Challenge: Accessing proprietary information unlawfully.
Solution: Ensure all information is obtained legally and ethically.
3. Ethical Dilemmas
Challenge: Balancing competitive advantage with fair business practices.
Solution: Establish clear ethical guidelines and adhere to industry codes of conduct.
4. Technical Complexities
Challenge: Reverse engineering sophisticated or proprietary technologies.
Solution: Invest in skilled personnel and advanced tools for accurate analysis.
5. Resource Intensity
Challenge: Reverse engineering can be time-consuming and costly.
Solution: Evaluate the return on investment and focus on high-impact areas.
Strategies for Responsible Reverse Engineering
1. Legal Due Diligence
Patent Searches: Identify existing patents and understand their scope.
Consult Legal Experts: Ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
2. Ethical Framework Establishment
Code of Conduct: Define ethical boundaries and expectations.
Transparency: Maintain open communication about methods and intentions.
3. Focus on Innovation
Value Addition: Aim to improve upon existing designs, not just replicate them.
Original Contributions: Develop unique features or technologies.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Interdisciplinary Teams: Involve experts from engineering, legal, and business fields.
Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of learning and innovation.
NorthnStar's Expertise in Reverse Engineering
At NorthnStar, we offer comprehensive services to help clients leverage reverse engineering responsibly and effectively.
Our Services Include:
Legal and Ethical Guidance: Ensuring compliance with IP laws and ethical standards.
Technical Analysis: Utilizing advanced tools and expertise to dissect and understand products.
Innovation Development: Transforming insights into innovative designs and solutions.
Prototyping and Testing: Building and validating new products based on reverse engineering findings.
Market Strategy Support: Assisting in positioning and launching new products.
Client Success Story:
Our collaboration with the automotive parts manufacturer exemplifies how reverse engineering can serve as a tool for innovation rather than mere replication. By focusing on adding value and adhering to ethical practices, we helped the client achieve significant market success and contribute positively to the industry.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering, when used responsibly, is a powerful tool for innovation and reinvention. It enables businesses to learn from existing products, improve upon them, and develop new solutions that meet market needs.
At NorthnStar, we're committed to helping you harness the potential of reverse engineering ethically and effectively. Let us guide you in transforming insights into innovative products that drive success.
Interested in exploring how reverse engineering can fuel your innovation? Contact NorthnStar today, and let's embark on this journey together.
Discover how reverse engineering serves as a catalyst for innovation and reinvention in product development. This article explores strategies, challenges, and ethical considerations, highlighting NorthnStar's expertise in leveraging reverse engineering responsibly.
Is reverse engineering merely a means to replicate existing products, or can it be a powerful catalyst for innovation and reinvention? By deconstructing products and systems, we can uncover insights that drive technological advancement and competitive advantage. Let's explore how reverse engineering serves as a tool for both innovation and reinvention.
At NorthnStar, we've encountered numerous clients intrigued by the potential of reverse engineering. They often face challenges in understanding complex technologies, improving upon existing products, or entering markets dominated by established players. Recognizing the strategic value and ethical considerations of reverse engineering, we've developed approaches to help them leverage this tool effectively. This article delves into the role of reverse engineering in product development, sharing insights from our experiences to guide you in harnessing its power for innovation and reinvention.
Understanding Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering involves dissecting a product or system to understand its components, architecture, and functioning. It's a process of deconstruction that reveals the intricacies of design and technology, enabling businesses to learn from existing solutions.
Applications of Reverse Engineering:
Product Improvement: Identifying weaknesses or limitations in a product to enhance performance.
Technology Learning: Gaining insights into advanced technologies used by competitors.
Legacy System Support: Maintaining or updating systems with obsolete documentation.
Innovation Catalyst: Inspiring new ideas by understanding how existing products work.
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights: Respecting patents, copyrights, and trade secrets is crucial.
Fair Use: Reverse engineering for interoperability or research may be permissible under certain conditions.
Compliance: Ensuring that the process adheres to relevant laws and industry regulations.
Case Study: Innovating Through Reverse Engineering in the Automotive Industry
Client Challenge:
An automotive parts manufacturer approached us with the goal of entering the electric vehicle (EV) market. They lacked expertise in EV technology and faced significant barriers due to proprietary technologies held by established competitors. They sought to understand the design and functionality of leading EV components to develop compatible and competitive products. Acknowledging the legal and ethical complexities, they turned to our expertise to navigate reverse engineering responsibly.
Our Approach:
We aimed to help the client leverage reverse engineering as a tool for innovation while ensuring compliance with all legal and ethical standards. Our multidisciplinary team collaborated with legal advisors, engineers, and industry experts to structure a strategic plan.
Actions Taken:
Feasibility Assessment:
Legal Review: Evaluated patents and IP protections related to target components.
Ethical Considerations: Established guidelines to prevent infringement and unethical practices.
Market Analysis: Identified opportunities where innovation could meet unmet needs.
Target Selection:
Component Identification: Chose specific parts with expired patents or without IP restrictions.
Focus on Improvement Areas: Targeted components known for performance issues or high failure rates.
Reverse Engineering Process:
Disassembly and Documentation:
Carefully disassembled components to study materials, construction, and design.
Documented findings meticulously, creating detailed diagrams and notes.
Analysis and Testing:
Performed material analysis to understand properties and limitations.
Conducted performance testing to benchmark against industry standards.
Innovation and Redesign:
Idea Generation:
Brainstormed enhancements based on insights gained.
Considered alternative materials, designs, and technologies to improve performance.
Prototyping and Development:
Developed prototypes incorporating innovative features.
Tested prototypes rigorously to ensure reliability and compatibility.
Compliance and Validation:
Legal Verification:
Ensured that new designs did not infringe on existing IP.
Filed for patents on novel innovations developed.
Certification:
Obtained necessary industry certifications and approvals.
Market Entry Strategy:
Value Proposition Articulation:
Highlighted improved performance, cost-effectiveness, or unique features.
Positioned products to meet specific market needs unmet by competitors.
Partnership Development:
Established relationships with EV manufacturers and suppliers.
Created collaborative opportunities for further innovation.
Outcome:
Successful Product Launch:
Introduced a line of EV components that offered superior performance and reliability.
Gained market traction by filling gaps left by competitors.
Innovation Recognition:
Received industry accolades for innovative designs.
Secured patents for new technologies developed.
Business Growth:
Expanded client portfolio and increased revenue streams.
Established the client as a credible player in the EV market.
Key Takeaways:
Strategic Targeting: Focusing on components with opportunities for innovation minimizes legal risks and maximizes impact.
Ethical Practices: Adhering to legal and ethical standards builds trust and long-term success.
Value Addition: Using reverse engineering to innovate rather than merely replicate creates competitive advantages.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involving legal, technical, and market experts ensures a holistic approach.
Reverse Engineering as a Tool for Innovation
1. Enhancing Existing Products
Identifying Limitations: Understanding weaknesses in current products opens avenues for improvement.
Incorporating New Technologies: Integrating advanced materials or technologies can elevate product performance.
2. Accelerating R&D
Learning from Competitors: Gaining insights into industry standards and best practices speeds up development.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Understanding why certain designs fail helps in avoiding similar mistakes.
3. Fostering Innovation
Inspiration Source: Existing products can spark ideas for entirely new solutions.
Cross-Industry Applications: Applying concepts from one industry to another can lead to breakthrough innovations.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
1. Intellectual Property Risks
Challenge: Unintentionally infringing on patents or copyrights.
Solution: Conduct thorough IP research and consult legal experts.
2. Trade Secret Violations
Challenge: Accessing proprietary information unlawfully.
Solution: Ensure all information is obtained legally and ethically.
3. Ethical Dilemmas
Challenge: Balancing competitive advantage with fair business practices.
Solution: Establish clear ethical guidelines and adhere to industry codes of conduct.
4. Technical Complexities
Challenge: Reverse engineering sophisticated or proprietary technologies.
Solution: Invest in skilled personnel and advanced tools for accurate analysis.
5. Resource Intensity
Challenge: Reverse engineering can be time-consuming and costly.
Solution: Evaluate the return on investment and focus on high-impact areas.
Strategies for Responsible Reverse Engineering
1. Legal Due Diligence
Patent Searches: Identify existing patents and understand their scope.
Consult Legal Experts: Ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
2. Ethical Framework Establishment
Code of Conduct: Define ethical boundaries and expectations.
Transparency: Maintain open communication about methods and intentions.
3. Focus on Innovation
Value Addition: Aim to improve upon existing designs, not just replicate them.
Original Contributions: Develop unique features or technologies.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Interdisciplinary Teams: Involve experts from engineering, legal, and business fields.
Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of learning and innovation.
NorthnStar's Expertise in Reverse Engineering
At NorthnStar, we offer comprehensive services to help clients leverage reverse engineering responsibly and effectively.
Our Services Include:
Legal and Ethical Guidance: Ensuring compliance with IP laws and ethical standards.
Technical Analysis: Utilizing advanced tools and expertise to dissect and understand products.
Innovation Development: Transforming insights into innovative designs and solutions.
Prototyping and Testing: Building and validating new products based on reverse engineering findings.
Market Strategy Support: Assisting in positioning and launching new products.
Client Success Story:
Our collaboration with the automotive parts manufacturer exemplifies how reverse engineering can serve as a tool for innovation rather than mere replication. By focusing on adding value and adhering to ethical practices, we helped the client achieve significant market success and contribute positively to the industry.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering, when used responsibly, is a powerful tool for innovation and reinvention. It enables businesses to learn from existing products, improve upon them, and develop new solutions that meet market needs.
At NorthnStar, we're committed to helping you harness the potential of reverse engineering ethically and effectively. Let us guide you in transforming insights into innovative products that drive success.
Interested in exploring how reverse engineering can fuel your innovation? Contact NorthnStar today, and let's embark on this journey together.
Other Blogs
Other Blogs
Check our other project Blogs with useful insight and information for your businesses
Other Blogs
Other Blogs
Check our other project Blogs with useful insight and information for your businesses
Other Blogs
Other Blogs
Check our other project Blogs with useful insight and information for your businesses